
Windows will install all needed drivers automatically, just the Intel NIC drivers for e1000 must be loaded from ISO (I got one big driver ISO from Intel containing all NIC drivers).
After success (the wizard just copies the data, means I got a 80 GB disk but only 5 GB data on it so it was just a few minutes for the whole process on a gigabit network) just change the boot device to the hard disk and start the VM. Now enter all commands from the wizard on the source server tells you (configure network and request the copy process). Become root and run fdisk (fdisk /dev/sda/) to make sure that sda is here, exit fdisk with 'w'. On the Proxmox VE host, prepare a KVM guest, make sure you got a big enough IDE disk assigned (add 1 GB extra to be on the safe side) and also boot this KVM guest with the live CD and execute a shell. Now, boot the physical host with Clonezilla, go for beginner mode and select device - device and then remote, just follow the wizard. Prepare the source host, make sure that you have standard IDE drivers enabled (for WinXP/Win2003 use the mergeide.reg ( File:Mergeide.zip) ), for W2k I followed this link (solution 2 worked for me):. 
This method is fast, reliable and OS independent as it uses live CDs. Physical-to-Virtual (P2V) Migration of physical servers to Proxmox VE Virtual-to-Virtual (V2V) Migration of virtual machines and containers from other hypervisors to Proxmox VE Physical-to-Virtual (P2V)įollow these steps to do a P2V migration and turn a physical machine into a Proxmox VE virtual machine that uses Qemu and KVM.
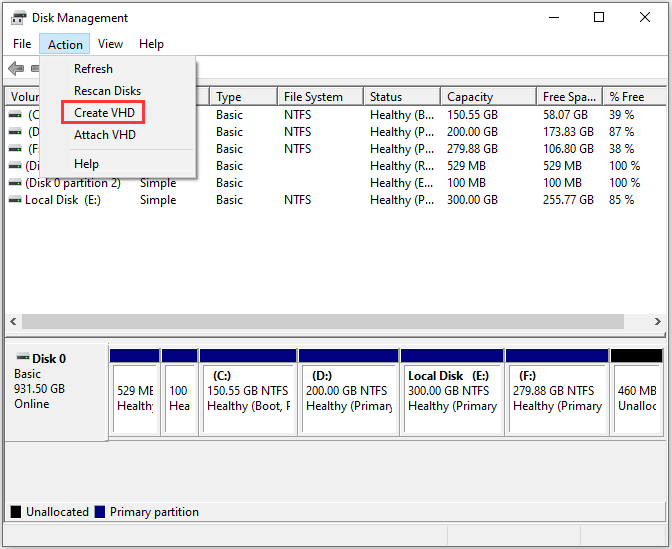
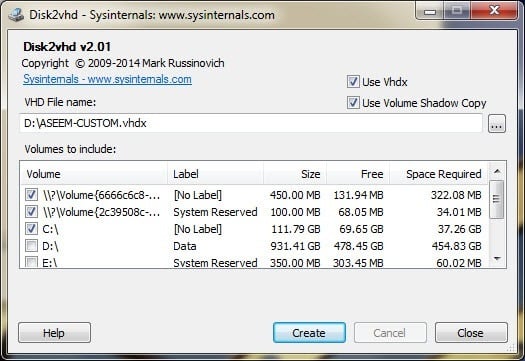
There are various ways to migrate existing servers to Proxmox VE.
2.2.3.2 Move the image to the Proxmox VE Server. 2.2.2 Prepare location to save local image.







 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
